Roux‑en‑Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) is a benchmark bariatric procedure that reduces stomach volume and reroutes food to alter absorption and gut hormones, producing substantial and durable weight loss.
Gastric Bypass
The Procedure (Key Steps)
• Creation of a ~30 ml gastric pouch using a stapler, separated from the remaining stomach.
• Division and measurement of small intestine; the alimentary limb is brought up and joined to the pouch.
• Gastro‑jejunal anastomosis completed; biliopancreatic limb later connected to restore flow of enzymes.
• Leak test performed before port closure.
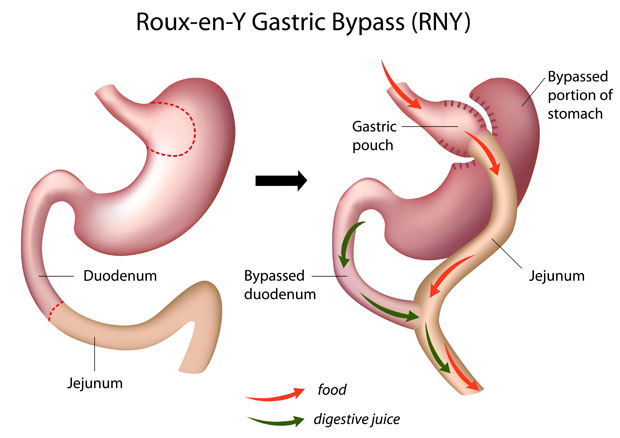
Expected Outcomes
• Typical excess‑weight loss: ~60–80%.
• Strong metabolic impact with frequent remission/improvement of type 2 diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidaemia.
Risks and Complications
• Mortality ≈0.09–0.15%; early complication rate ≈5.9–6.8%.
• Anastomotic stenosis (~2%): dysphagia/reflux; may require endoscopic dilatation; avoid smoking and chronic NSAIDs.
• Staple‑line/anastomotic bleeding (~2%).
• Anastomotic leak (≈1–2%).
• Internal hernia/obstruction (~1%).
• Dumping syndrome; bowel habit change (up to ~1 in 3 with high‑fat intake).
• Gallstones: risk increased; prophylaxis may be prescribed; cholecystectomy if symptomatic.
• Nutritional deficiencies: B12, thiamine (B1), iron, calcium, vitamin D, copper, zinc, selenium, vitamin A—lifelong supplements and monitoring.
Other Gastric Bypass Variations
• One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB): long narrow pouch anastomosed to jejunum (~150–200 cm). Early serious complications ≈0.1–0.2%; re‑operation in ~5% long‑term (malnutrition or severe reflux). Requires lifelong supplements.
• Single Anastomosis Duodeno‑Ileal Bypass (SADI‑S) and Single Anastomosis Sleeve‑Ileal (SASI‑S): combine sleeve with a single intestinal bypass; effective for weight loss and diabetes control but require close nutritional surveillance.
Why Dr. Spyros Panagiotopoulos?
Mr. Panagiotopoulos is highly experienced in RYGB and advanced variations (OAGB/SADI‑S/SASI‑S). He prioritises meticulous technique, careful patient selection and rigorous long‑term aftercare.
